Electrical and Computer Engineering
Bachelor of Science in Electrical and Computer Engineering
The Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering program, with a focus on Electrical and Computer Engineering (ECE) of VinUniversity, was developed based on the Cornell ECE program and validated by Cornell University. The overall aim of the program is to nurture and develop young leaders in Electrical and Computer Engineering with clear direction and vision, creativity and sound personal values; who pave the way for the development of science and technology, to increase labor productivity and to benefit society.
Career Prospects of an Electrical and Computer Engineering Graduate
Enrolling in the ECE program at VinUniversity will aid you in cultivating essential skills and gaining valuable employment experiences highly sought after by academic institutions, employers, and professional bodies. Graduates of this program are highly esteemed by a wide range of employers, spanning local, national, and international sectors. With a critical shortage of skilled engineers globally, graduates of the ECE program are in high demand across various sectors with attractive packages, including automotive, electronics manufacturing, semiconductor, robotics, renewable energy, telecommunications, smart health and more.
Our dedicated Career Development Office provides support and guidance to students, helping them explore career pathways, secure internships and job placements, and prepare for a successful transition into the workforce. Furthermore, numerous proactive graduates have embraced entrepreneurship, founding new startups that pioneer inventive applications of Electrical and Computer Engineering technologies.
Post-graduate Study
VinUniversity’s commitment to academic excellence is truly commendable, especially with its offering of fully supported integrated degree and doctoral programs through scholarships. This initiative not only fosters advanced research and innovation but also ensures that aspiring scholars have the resources they need to pursue their academic goals.
Destination/List of Partner Universities
- Cornell University, USA (Engineering and Computer Science, Business and Management)
- University of California San Diego, USA (Engineering and Computer Science)
- University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, USA (Engineering and Computer Science)
- University of Pennsylvania, USA (Engineering and Computer Science)
- University of Technology Sydney, Australia (Engineering and Computer Science)
- The University of Queensland, Australia (Engineering and Computer Science)
- Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (Engineering and Computer Science, Business and Management)
The remarkable achievement of approximately 27 CECS students, comprising nearly 44% of Corhot 1, gaining acceptance into integrated degree and doctoral programs at partner universities, is truly commendable. These collaborative joint programs not only offer students the chance to pursue advanced education at prestigious institutions but also signify the recognition of VinUniversity’s academic quality and the caliber of its students.
By providing access to top-tier postgraduate studies and fostering collaborations with esteemed institutions, VinUniversity demonstrates its dedication to nurturing the next generation of scholars and innovators, poised to make significant contributions to their fields and society as a whole.
Industry Career
With your background in electrical and computer engineering, covering a broad of areas including circuits, communication, control, computer architecture, electromagnetics, signal processing, optics, solid state, and power, you have the capacity to make substantial contributions across diverse industries. Below are some roles (but not exhaustive) that may align with your interests:
1. Embedded Systems Engineer
- Role description: An Embedded Systems Engineer is responsible for designing, developing, and testing embedded systems, which are specialized computing systems that perform dedicated functions within larger systems or devices for various industries such as automotive, consumer electronics, medical devices, and industrial automation.
- Required Skills: Proficiency in programming languages (C/C++, Assembly), microcontroller architectures, embedded systems
- Potential Companies: Intel Corporation, Qualcomm Incorporated, Texas Instruments, ARM Holdings, STMicroelectronics, MediaTek Inc., Renesas Electronics Corporation, FPT Software, Viettel, Samsung Electronics Vietnam, Intel Products Vietnam, Bosch Vietnam, NXP Semiconductors Vietnam, and Panasonic Vietnam.
2. IC Design Engineer
- Role description: As an IC Design Engineer, you are responsible for designing and developing integrated circuits (ICs) or chips used in various electronic devices. You will work on designing circuitry, optimizing performance, and ensuring functionality within specified parameters.
- Required Skills: Proficiency in IC design tools like Cadence Virtuoso, Synopsys Design Compiler, or Mentor Graphics. Solid understanding of semiconductor physics and CMOS technology. Knowledge of RTL design, Verilog, VHDL, and digital/analog circuit design. Experience with verification techniques, such as simulation, formal verification, and timing analysis. Strong problem-solving skills and attention to detail.
- Potential Companies: Intel Corporation, Qualcomm Incorporated, Broadcom Inc., NVIDIA Corporation, Samsung Electronics, TSMC, GlobalFoundries, FPT Semiconductor, and Viettel Semiconductor
3. Telecommunications Engineer
- Role description: A Telecommunications Engineer designs, implements, and maintains communication networks and systems, including wired and wireless infrastructure. They work on various aspects of network architecture, such as routing, switching, and transmission, to ensure reliable and efficient data transmission. Responsibilities may include network planning, installation, configuration, troubleshooting, and performance optimization.
- Required Skills: Proficiency in networking protocols and technologies (TCP/IP, Ethernet). Knowledge of telecommunications systems, including voice, data, and video transmission. Experience with network equipment and tools, such as routers, switches, and network analyzers. Ability to troubleshoot complex network issues and implement solutions. Familiarity with network security principles and practices. Strong analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Potential Companies: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Nokia Corporation, Ericsson, Cisco Systems, Inc., VNPT, FPT Telecom, MobiFone.
4. Electronics Design Engineer
- Role description: An Electronics Design Engineer is responsible for conceptualizing, designing, prototyping, and testing electronic circuits and systems. They work on various stages of product development, from initial concept through to production, ensuring that the electronic components meet performance, reliability, and cost requirements.
- Required Skills: Proficiency in PCB design software such as Altium Designer, Cadence Allegro, or EagleCAD. Strong understanding of analog and digital circuit design principles, including signal processing, amplification, filtering, and microcontroller interfacing. Experience with programming microcontrollers using languages like C/C++ or assembly language.
- Potential Companies: Intel Corporation, Texas Instruments, Samsung Electronics, Viettel, NXP Semiconductors Vietnam.
5. Robotics Engineer
- Role description: Robotics Engineers design robotic systems, including their mechanical structure, electronics, and software components. They work on creating systems that can perform tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously.
- Required Skills: Knowledge of mechanical design principles and materials to build robust and efficient robotic systems. Understanding of electronics and control systems to design and integrate sensors, actuators, and other electrical components. Proficiency in programming languages such as C/C++, Python, and ROS (Robot Operating System) for developing control algorithms and software.
- Potential Companies: Boston Dynamics, iRobot Corporation, ABB Robotics, KUKA Robotics, FPT Corporation, Advanced Robotics & Automation Research JSC (ARAR)
6. Signal Processing Engineer
- Role description: Signal Processing Engineers are responsible for analyzing, modifying, and synthesizing signals (such as sound, images, and data) to extract relevant information or enhance their quality. They develop algorithms and mathematical models for processing signals efficiently and accurately and/or utilize DSP techniques and tools to manipulate digital signals in real-time or offline.
- Required Skills: Strong knowledge in mathematical model, digital signal processing (DSP), programming languages (MATLAB, Python with libraries like NumPy and SciPy, C/C++), algorithm design, signal processing tools.
- Potential Companies: Intel Corporation, Texas Instruments, Qualcomm, MathWorks, Viettel, VNPT.
7. Renewable Energy Engineer
- Role description: Renewable Energy Engineers are professionals responsible for designing, developing, and implementing renewable energy systems. They work on projects related to solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biomass energy. Their role involves conducting feasibility studies, designing systems, overseeing installation processes, and ensuring the efficient operation of renewable energy projects. They also contribute to research and development efforts to improve renewable energy technologies and enhance their integration into existing infrastructure.
- Required Skills: Strong understanding of renewable energy technologies and systems, including solar photovoltaic (PV), wind turbines, hydroelectric generators, geothermal systems, and biomass energy. Ability to design and analyze renewable energy systems, including performing simulations, conducting energy audits, and optimizing system performance.
- Potential Companies: Tesla, Inc., Vestas Wind Systems, GE Renewable Energy, Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, Ormat Technologies, SunPower.
Start-up
At VinUniversity, we foster a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship, empowering our students to turn their ideas into impactful ventures. Through our Entrepreneurship Lab (E-lab), we provide a supportive ecosystem where students can explore, develop, and launch their startup projects. From ideation to execution, we offer mentorship, networking opportunities, and access to resources to help budding entrepreneurs succeed. Some of outstanding startup projects led by ECE students include:
- NaviAI JSC., pioneering AI-driven navigation solutions.
- MindPal Labs, dedicated to a team of AI Agents that know it all and do it all.
These projects exemplify VinUniversity’s commitment to nurturing creativity, innovation, and social impact, ensuring that our students are equipped with the entrepreneurial mindset and skills to thrive in today’s dynamic world.
Program overview
Program Profile
| Name of the degree | Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering |
| Name of the program | Electrical and Computer Engineering (ECE) |
| Program duration | To be completed in 4 years on a full-time basis |
| Total credits | Option 1 Single major: 122 credits
Option 2 Major + minor in Robotics or Product Design or Artificial Intelligence or another minor: 137 credits |
Concentration description
1. Computer Engineering
- Computer Engineering focuses on the design, development, and integration of computer systems and their hardware and software components such as integrated circuits (IC), embedded systems.
- Students learn about IC design, computer networks, IC design for Artificial Intelligence and Machine learning
- Career opportunities include roles in computer hardware design, software development, embedded systems engineering, network engineering, and robotics.
2. Communications and Signal Processing
- This concentration emphasizes the transmission, reception, processing, and analysis of signals for communication purposes (wire and wireless).
- Students study topics such as digital signal processing, wireless communications, data compression, modulation techniques, and error control coding.
- Career paths include telecommunications engineering, wireless networking, audio and video processing, radar systems, and sensor networks.
3. Control and Automation
- Control and Automation deals with the design and implementation of systems to control and regulate processes, machinery, and devices.
- Students learn about control theory, system modeling, feedback systems, robotics, mechatronics, and industrial automation.
- Career opportunities include roles in industrial automation, robotics engineering, process control, automotive control systems, and aerospace systems.
4. Power and Green Energy
- This major focuses on the generation, distribution, and utilization of electrical power, with an emphasis on sustainability and renewable energy sources.
- Students study topics such as power generation technologies, electrical grid systems, renewable energy integration, energy efficiency, and power electronics.
- Career paths include power system engineering, renewable energy development, smart grid technologies, energy management, and sustainable infrastructure design.
Program Purpose
The overall aim of the program is to nurture and develop young leaders in electrical engineering with clear direction and vision, creativity and sound personal values; who pave the way for the development of science and technology, to increase labor productivity and to benefit society.
Program Educational Objectives
The educational objectives of the Bachelor of Science in Electrical and Computer Engineering program are that within a few years of graduation, a majority of our graduates will demonstrate excellence in top graduate programs; or in technical and managerial leadership tracks in technology-based industries or other sectors; or pursuing entrepreneurial ventures. In these roles, they will:
- Apply basic knowledge of electrical and computer engineering principles and in-depth knowledge of one area of concentration to solve a full range of technical and societal problems;
- Conceive, design, and realize products, systems, and services, while properly respecting economic, environmental, cultural, safety, and ethical standards or constraints;
- Be leaders with an entrepreneurial mindset, effective communicators, and informed decision makers as members of multidisciplinary teams, supporting collaborative and inclusive environments;
- Discover and apply new knowledge, and engage in life-long learning for the profession of electrical and computer engineering;
- Engage with their communities, profession, the nation, and the world.
Student Outcomes
- An ability to identify, formulate, and solve complex engineering problems by applying principles of engineering, science, and mathematics;
- An ability to apply engineering design to produce solutions that meet specified needs with consideration of public health, safety, and welfare, as well as global, cultural, social, environmental, and economic factors;
- An ability to communicate effectively with a range of audiences;
- An ability to recognize ethical and professional responsibilities in engineering situations and make informed judgments, which must consider the impact of engineering solutions in global, economic, environmental, and societal contexts;
- An ability to function effectively on a team whose members together provide leadership, create a collaborative and inclusive environment, establish goals, plan tasks, and meet objectives;
- An ability to develop and conduct appropriate experimentation, analyze and interpret data, and use engineering judgment to draw conclusions;
- An ability to acquire and apply new knowledge as needed, using appropriate learning strategies;
Why is ECE Right for You?
In today’s world, characterized by the proliferation of sustainable energy, smart home technology, and the Internet of Things, Electrical and Computer Engineering stands at the forefront of innovation and progress. At VinUniversity, the ECE program is designed to equip students with the knowledge, skills, and hands-on experience needed to excel in this dynamic field.
The ECE program offers a comprehensive curriculum covering a broad spectrum of topics within the field including both software and hardware. From the fundamentals of computer engineering, programming languages, circuit theory and electronics to advanced subjects such as micro-electronic chip design, power systems, signal processing, telecommunications, and renewable energy technologies, students gain a deep understanding of the discipline’s core principles and emerging trends.
Join us at CECS and embark on a rewarding journey in Electrical and Computer Engineering, where innovation meets impact, and endless possibilities await.
Curriculum structure
| No. |
Curriculum Components |
Number of Credits | Credit Distribution (%/Total Credits) |
| I | VINCORE | 31 | 25.4% |
| I.1 | Enterprise and Innovation | 4 | 3.3% |
| I.2 | Leadership Mindset | 2 | 1.6% |
| I.3 | Civic Responsibility | 2 | 1.6% |
| I.4 | Ethics | 2 | 1.6% |
| I.5 | Community Service Learning | 45 hours | |
| I.6 | Working with the Brain | 2 | 1.6% |
| I.7 | Working with Technology | ||
| I.8 | Working with Others | 4 | 3.3% |
| I.9 | Working with the Self | 90 hours | |
| I.10 | Integrated Vietnam Studies | 11 | 9.0% |
| I.11 | Sustainability and Global Citizenship | 2 | 1.6% |
| I.12 | Creative Arts | 2 | 1.6% |
| II | PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION | 91 | 74.6% |
| II.1 | College Core Requirement | 39 | 32% |
| II.2 | Major Core Requirement | 19 | 15.6% |
| II.3 | Major Foundation Requirement | 15 | 12.3% |
| II.4 | Area of Concentration (Elective) | 12 | 9.8% |
| II.5 | Minor* | 15* | |
| II.6 | Internship/Co-op | 640 hours | |
| II.7 | Capstone Design | 6 | 4.9% |
| TOTAL | 122 (137)* | 100% |
* Students are required to complete a minimum of 122 earned credits to graduate. They have the option to take up to 137 earned credits within the allowed timeframe without incurring additional tuition fees.
Course flow
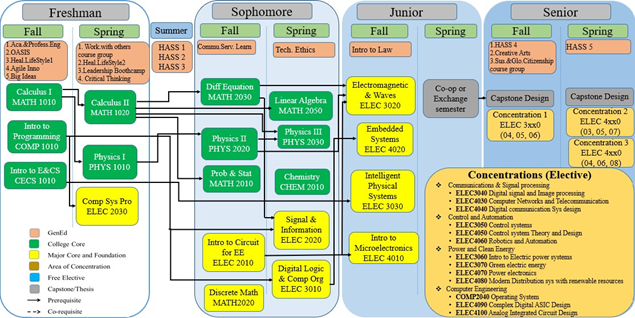
Course flow – Main track
For more detailed information about our Electrical Engineering curriculum framework, please read here.
Course description
3 credits
Pre-requisites: Calculus II
Taking with Linear Algebra simultaneously is not recommended.
Course Description:
This course gives an introduction to ordinary and partial differential equations. Topics include first order equations (separable, linear, homogeneous, exact); mathematical modelling (e.g., population growth, terminal velocity); qualitative methods (slope fields, phase plots, equilibria and stability); numerical methods; second order equations (method of undetermined coefficients, application to oscillations and resonance, boundary value problems and eigenvalues); and Fourier series. A substantial part of this course involves partial differential equations, such as the heat equation, the wave equation, and Laplace’s equation.
3 credits
Pre-requisites: High school chemistry
Course Description:
This course covers basic chemical concepts, such as reactivity and bonding of molecules, introductory quantum mechanics, and intermolecular forces in liquids and solids and gases. Attention will be focused on aspects and applications of chemistry most pertinent to engineering.
3 credits
Pre-requisites: Physics I
Course Description:
This course covers electrostatics, the behavior of matter in electric fields, DC circuits, magnetic fields, Faraday’s law, AC circuits, and electromagnetic waves.
2 credits
Pre-requisites: Physics II (Electromagnetism), Calculus II
Course Description:
This course covers the physics of oscillations and wave phenomena, including driven oscillations and resonance, mechanical waves, sound waves, electromagnetic waves, standing waves, Doppler effect, polarization, wave reflection and transmission, interference, diffraction, geometric optics and optical instruments, wave properties of particles, particles in potential wells, light emission and absorption, and quantum tunnelling.
4 credits
Co-requisites: Differential Equations and Physics II
Course Description:
This course establishes the fundamental properties of circuits with application to modern electronics. Topics include circuit analysis methods, operational amplifiers, basic filter circuits, and elementary transistor principles. The laboratory experiments are coupled closely with the lectures.
4 credits
Pre-requisites: Differential Equations, Introduction to Programming
Corequisite: Linear Algebra
Course Description:
This course teaches introduction to signal processing. Topics include frequencybased representations: Fourier analysis and synthesis; discrete-time linear systems: input/output relationships, filtering, spectral response; analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion; continuous time signals and linear timeinvariant systems: frequency response and continuous-time Fourier transform.
3 credits
Pre-requisites: Introduction to Programming
Course Description:
This course provides a strong foundation in the principles, practices, and art of computer systems programming using the C and C++ programming languages. Students will learn procedural programming in C and how to theoretically analyse and practically implement basic data structures and algorithms. Students will transition to C++ to explore object-oriented, generic, functional, and concurrent programming before exploring advanced data structures and algorithms involving trees, tables, and graphs. Students will explore systems programming using the POSIX standard library. The course includes a series of programming assignments for students to put the principles they have learned into practice.
4 credits
Pre-requisites: Introduction to Programming
Course Description:
This course provides an introduction to the design and implementation of digital circuits and microprocessors. Topics include transistor network design, Boolean algebra, combinational circuits, sequential circuits, finite state machine design, processor pipelines, and memory hierarchy. Design methodology using both discrete components and hardware description languages is covered in the laboratory portion of the course.
4 credits
Pre-requisites: Physics II, Differential equations, Introduction to Circuits for Electrical Engineers
Course Description:
This course covers static, quasi-static, and dynamic electromagnetic fields and waves. Topics include Maxwell’s equations (integral and differential forms), fields of charge and current distributions, boundary conditions, fields near conductors, method of images, material polarization and dielectrics; energy, work, and power in electromagnetic systems; wave propagation and polarization, waves in media (dielectrics, conductors, and anisotropic materials); reflection, transmission, and refraction at media interfaces; guided waves in transmission lines, Smith charts, transients; metallic and dielectric waveguides; radiation and antennas, antenna arrays, electric circuits for transmission and reception, aperture antennas and diffraction.
3 credits
Pre-requisites: Introduction to Engineering, Programming language
Course Description:
This is an interdisciplinary design project course which involves students from different engineering and computer science programs. In this course, students will engage in a holistic design approach to Intelligent Physical Systems which can perceive, reason about, and act upon their environment. This course includes topics on algorithms, sensors, actuators, power, and mechanics. Students will learn the value and trade-offs between theory, simulation, and physical implementations, and gain familiarity with rapid prototyping techniques, system debugging, teamwork, leadership skills, time management, and how to disseminate work to a broader audience through wiki-pages.
4 credits
Pre-requisites: Signals and Information
Course Description:
This course focuses on developing a toolbox of techniques to process and analyse real-world signals, model them under uncertainty/noise, and make decisions about them. Highlights of the course will include sampling, filtering, multirate signal processing, intro to statistical signal processing including Wiener and Kalman filtering, and the foundations of computer vision. The course will aim to include a broad range of applications including audio/music, imaging, and data analytics. The coursework includes a design project to emphasize design experiences.
4 credits
Pre-requisites: Introduction to Circuits for Electrical Engineers
Course Description:
This course covers the analysis and design of control systems with emphasis on modelling, state variable representation, computer solutions, modern design principles, and laboratory techniques. Topics include Modelling and dynamic response, Root locus design method, Frequency response design methods, Statespace design.
3 credits
Pre-requisites: Signals and Systems
Course Description:
This course teaches modern electric power system modelling, analysis, and computation with a focus on analysis techniques appropriate for power system modelling, analysis, and power flow computation. Topics include transmission line models, transformers and per unit system, generator models, network matrices, power flow analysis and computation, real and reactive power control, voltage control, economic dispatch.
3 credits
Pre-requisites: Introduction to Circuits for Electrical Engineers
Course Description:
This course provides a quantitative, practical introduction to a wide range of renewable energy systems. Topics include wind resource and turbines, Photovoltaic Cells, Solar Resource, Photovoltaic Systems, energy and financial performance of green energy projects; integration of green energy into the power grid, Demand Side Management, Economics of Energy Efficiency.
4 credits
Pre-requisites: Introduction to Circuits for Electrical Engineers
Course Description:
This course introduces the basic devices and circuits in modern microelectronics. Students learn not only basic structures and operations of semiconductor devices through simple models (diodes, CMOS, and BJT) but also how to analyse and design basic transistor modules in digital and analog circuits including biasing, amplifiers, filters, logic gates, and memory. The course introduces intuitive design methods to map circuit specifications to transistor topology, as well as first-order time-constant estimation. SPICE and measurement labs accompany the progress in lectures for hands-on experiences.
4 credits
Pre-requisites: Digital Logic and Computer Organization
Course Description:
This course provides an introduction to the design of embedded systems, with an emphasis on understanding the interaction between hardware, software, and the physical world. Topics covered include assembly language programming, interrupts, I/O, concurrency management, scheduling, resource management, and real-time constraints.
4 credits
Pre-requisites: Embedded Systems
Course Description:
This course teaches basic networking with an emphasis on the Internet. Examples of topics include the World Wide Web, Email and Peer to Peer networks, data transmission and data encoding, circuit vs. packet switching, local area network technology, routing and switching, congestion control, network security, wireless networks, and multimedia. Though the emphasis will be on the Internet, application modules on 4G/5G cellular, WiFi (802.11), and Bluetooth will be presented.
4 credits
Pre-requisites: Probability and Statistics, Signals and Information
Course Description:
The course covers communication theory, transceiver algorithms that enable reliable communication, wireless channels, and modern communication standards (such as 3GPP LTE and WiFi). The students will design a working audio band communication system that relies on orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM).
4 credits
Pre-requisites: Control Systems
Course Description:
This course covers System modelling and analysis, System structural properties, Feedback system design, Optimum feedback control, Introduction to the minimum principle.
4 credits
Pre-requisites: Control Systems
Course Description:
This course introduces fundamental concepts in robotics and applications. Topics include basics of manipulators, coordinate transformation and kinematics, trajectory planning, control techniques, sensors and devices, robot applications in industrial automation.
3 credits
Pre-requisites: Introduction to Circuits for Electrical Engineers
Course Description:
This course teaches major power electronics concepts, from both systems and components perspectives and design considerations for switching power conversion. Topics include switching conversion and analysis, DC-DC converters, rectifiers and switched capacitor circuits, inverters, power semiconductors in converters, feedback control for converters, control modeling, and design, AC-AC conversion, resonance in converters.
3 credits
Pre-requisites: Introduction to Electric Power Systems
Course Description:
This course teaches the operation of modern electric power distribution systems with the integration of renewable energy sources. Topics include the operation of distribution systems, power quality, solar power systems, wind power systems, system efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.


